The under absorption and over absorption of overhead
This differs from variable costing, which only allocates variable costs to units and treats fixed costs as period expenses. Moreover, variable costing results in a single lump-sum spending line item for fixed overhead expenditures for calculating net income on the income statement. Each unit of a produced good can now carry subject to change an assigned total production cost. This eliminates the distinctions between fixed and variable costs, thereby reflecting the impact of overhead on manufacturing. The entire issue of overhead absorption can be reduced by using just-in-time systems to reduce the amount of inventory on hand at the end of an accounting period.
Absorption Costing vs. Variable Costing Example
It provides a straightforward and rigorous costing tool for active enterprises. It also takes into account fluctuating turnover because costs have been allocated to the items. As you can see, the AC method assigns the cost of the workers’ wages and the utility expenses to the merchandise being produced. In many ways, this is a more accurate way to account for the true cost of producing the products. Absorption costing is typically used in situations where a company wants to understand the full cost of producing a product or providing a service. This includes cases where a company is required to report its financial results to external stakeholders, such as shareholders or regulatory agencies.
Related AccountingTools Courses
The salaries and benefits of supervisors and managers overseeing the production process are classified as fixed manufacturing overhead. (c) There includes no differentiation made between fixed and variable production costs. Absorption costing is normally used in the production industry here it helps the company to calculate the cost of products so that they could better calculate the price as well as control the costs of products. Maybe calculating the Production Overhead Cost is the most difficult part of the absorption costing method.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
In summary, absorption costing provides a comprehensive look at per unit costs by incorporating all expenses related to production. This aids pricing strategies and gives an accurate inventory valuation. The tradeoff is that net profit fluctuates more than with variable costing methods. Understanding these basics helps explain the meaning and utility of absorption costing.
- This can make it somewhat more difficult to determine the ideal pricing for a product.
- The actual amount of manufacturing overhead that the company incurred in that month was $98,000.
- As a result, profits get subtracted from the time in which they take place.
- If the prime cost of a unit is $200, the absorption rate per unit will be $50.
This method is suitable for labor-intensive industries in which manual labor is a dominant factor in production. If the prime cost of a unit is $200, the absorption rate per unit will be $50. This method is usually applied in cases where labor is the main factor in production. It is also applied when the quality, skill, and gender of employees do not differ significantly. This application of overheads is called absorption, which can be defined as the charging of overheads to production. This involves taking each cost center and applying its overheads to all the products that pass through it.
If a company prepares to ramp up production in preparation for a seasonal sales surge, this is an important factor to consider. The treatment of Overhead expenses is the fundamental difference between variable and absorption costing. (e) Because product costs comprise both fixed and variable costs, stocks are valued at full cost. In February, Higgins produced 60,000 widgets, so it allocated $120,000 of overhead. The actual amount of manufacturing overhead that the company incurred in that month was $109,000. Under this method, prime cost is used as the basis for determining the overhead absorption rate.
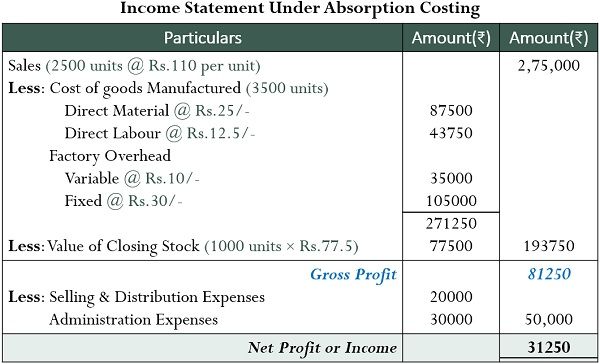
If price per unit sold is $4.5, calculate net income under the absorption costing and reconcile it with variable costing net income which comes out to be $20,727. As you can see, by allocating all manufacturing costs to inventory, absorption costing provides a more comprehensive assessment of profitability. In summary, the overhead absorption rate helps allocate a fair share of indirect overheads to each product based on expected production volume. Absorbed overhead is manufacturing overhead that has been applied to products or other cost objects. Overhead is usually applied based on a predetermined overhead allocation rate. Overhead is overabsorbed when the amount allocated to a product or other cost object is higher than the actual amount of overhead, while the amount is underabsorbed when the amount allocated is lower than the actual amount of overhead.
These materials can be easily traced to a specific product, such as raw materials and components. It reveals inefficient or efficient production resource utilization by displaying under- or over-absorption of manufacturing overheads. Examine each action to understand how it ties to the manufacturing process.
Since absorption costing requires the allocation of what may be a considerable amount of overhead costs to products, a large proportion of a product’s costs may not be directly traceable to the product. Fixed manufacturing overhead costs remain constant regardless of the level of production. These include expenses like rent for the manufacturing facility, depreciation on machinery, and salaries of supervisors. Also, it includes direct material costs, direct labor expenses, and variable production overheads.

