Direct materials quantity variance explanation, formula, reasons, example

An adverse or unfavorable material quantity variance occurs when the actual volume of materials used in production exceeds the standard quantity that is expected for the level of output in a period. This involves looking beyond the numbers to understand the underlying factors contributing to the variances. For example, if a material price variance is detected, managers should examine market conditions, supplier performance, and procurement strategies to pinpoint the cause. Similarly, if a material quantity variance is found, a thorough review of the production process, employee performance, and equipment efficiency is necessary. This investigative approach ensures that corrective actions are targeted and effective. Direct materials actually cost $297,000, even though the standard cost of the direct materials is only $289,800.
Do you own a business?
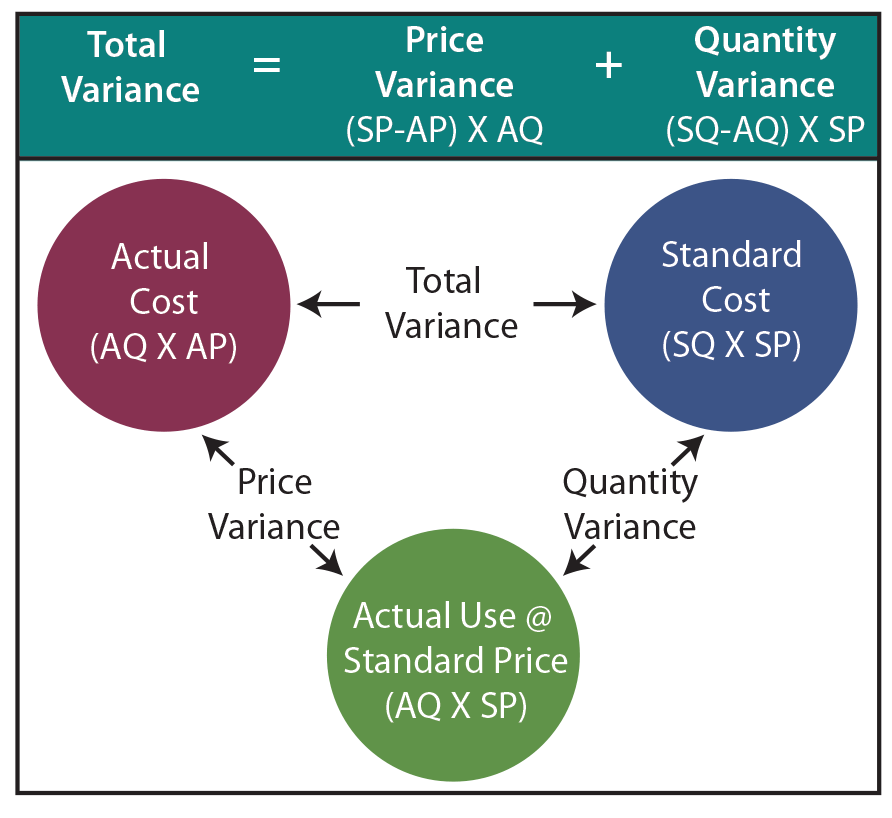
The standard cost of actual quantity purchased is calculated by multiplying the standard price with the actual quantity. This amount will represent the expected expenditure on direct material for this many units. The difference between this actual expenditure and the actual expenditure on direct material is the direct materials price variance.
- As businesses strive for greater precision in cost management, advanced techniques in variance analysis have become increasingly valuable.
- Practical capacity is used so that idle capacity may be found and put to better use.
- Inefficient production processes, outdated machinery, or inadequate employee training can result in higher material consumption than planned.
- When your business purchases others goods to produce your products, you must incorporate the cost of the supplies into your budgets at the beginning of the year and each month.
2: Direct Materials Cost Variance
To begin with, calculating direct material variance involves comparing the standard cost of materials to the actual cost incurred. This comparison helps businesses understand whether they are spending more or less than anticipated on raw materials. The standard cost is typically derived from historical data, industry benchmarks, or predetermined budgets, while the actual cost is recorded during the production process. The variance is calculated using the direct materials quantity variance formula, which takes the difference between the standard quantity and the actual quantity, and multiplies this by the standard price per unit of material.
Direct Material Quantity Variance FAQs
By understanding these trends, companies can anticipate future variances and take proactive measures to mitigate them. Analyzing direct material variance is a powerful tool for businesses aiming to maintain cost control and enhance profitability. By delving into the specifics of variances, companies can uncover inefficiencies and make informed decisions to optimize their operations.
In food service, the price of ingredients, such as milk and eggs, is always changing. When your business purchases others goods to produce your products, you must incorporate the cost of the supplies how to write an invoice – common types of invoices into your budgets at the beginning of the year and each month. Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners.
How do I calculate direct material price variance?
In such cases, the responsibility of any unfavorable quantity variance would lie on the purchasing department. Irrespective of who appears to be responsible at first glance, the variance should be brought to the attention of concerned managers for quick and timely remedial actions. As is the case when analyzing other variances, the direct material price variance needs to be assessed in the context of other relevant variances and factors, such as direct material price variance and direct labor variances. The management therefore needs to assess performance while taking all these relevant factors into account. The direct materials quantity variance of Blue Sky Company, as calculated above, is favorable because the actual quantity of materials used is less than the standard quantity allowed.
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. If the balance is considered insignificant in relation to the size of the business, then it can simply be transferred to the cost of goods sold account. Mark P. Holtzman, PhD, CPA, is Chair of the Department of Accounting and Taxation at Seton Hall University. He has taught accounting at the college level for 17 years and runs the Accountinator website at , which gives practical accounting advice to entrepreneurs. This formula is critical for understanding how actual spending tracks against estimations.
Knowledge of this variance may prompt a company’s management team to increase product prices, use substitute materials, or find other offsetting sources of cost reduction. In a multi-product company, the total quantity variance is divided over each of the products manufactured. Lumber costs may rise due to increased fuel costs and then lower when diesel prices stabilize.
For example, regression analysis might reveal that a 10% increase in supplier lead time results in a 5% increase in material quantity variance. Armed with this knowledge, companies can focus their efforts on improving supplier lead times to achieve better cost control. Additionally, the use of variance decomposition allows businesses to break down complex variances into more manageable components, providing deeper insights into specific areas of concern. It’s important to note that direct material variance can be broken down into more specific components, such as price and quantity variances.
A material quantity variance is the difference between the actual amount of materials used in the production process and the amount that was expected to be used. The measurement is employed to determine the efficiency of a production process in converting raw materials into finished goods. Material quantity variance is favorable if the actual quantity of materials used in manufacturing during a period is lower than the standard quantity that was expected for that level of output. Where,SQ is the standard quantity allowed,AQ is the actual quantity of direct material used, andSP is the standard price per unit of direct material. Another advanced technique is the application of statistical methods, such as regression analysis, to understand the relationship between different variables affecting material costs. By analyzing historical data, businesses can identify key drivers of variances and quantify their impact.

